Understanding the intricacies of nevada climate and weather is key to truly experiencing the Silver State, whether you’re planning a desert adventure, a mountain getaway, or simply interested in the forces shaping this unique landscape. While weather dictates your daily attire, climate informs the entire environment, influencing everything from the state’s diverse ecosystems to the rhythms of life and travel throughout the year. Delving into Nevada’s atmospheric patterns reveals a fascinating interplay of geography, scientific principles, and real-world impacts that every visitor and resident should appreciate.
Weather and Climate: The Core Differences
Weather describes the atmospheric conditions in a specific location over a short period. Think of it as the immediate report – temperature, humidity, wind, precipitation – that can change within minutes, hours, or days. It’s the reason you choose an umbrella today.
Climate, on the other hand, is the typical, expected weather for a place or region evaluated over a long timescale, usually 30 years or more. It’s the summary of those daily weather patterns, including averages, extremes, and variability. Climate helps you decide what kind of wardrobe you need year-round. Every corner of the world has its distinct normal climate, and understanding the nevada climate and weather involves appreciating its wide-ranging norms and potential extremes.
The Science Behind Atmospheric Conditions
Meteorology is the scientific study of the atmosphere focused on short-term weather prediction. Meteorologists use real-time data from weather stations, satellites, radar, and balloons to create forecasts, typically for the next seven to ten days.
Climatology examines the large-scale, long-term drivers of weather, including past and future climate trends. Climatologists analyze historical data and use complex models to understand how climate shapes environments and predict future conditions. This information is invaluable for long-term planning across various sectors, from agriculture to urban development and even tourism planning. You might encounter climate information in unexpected places; for instance, gardeners selecting plants often rely on USDA plant hardiness zones, which are determined by averaging decades of minimum winter temperatures – a direct application of climate data.
Navigating Nevada’s Unique Climate
Nevada holds the title of the driest state in the U.S., yet it is profoundly shaped by its mountainous terrain. The name “Nevada” itself means “snow-capped” in Spanish, a nod to the critical role mountain snow plays in supplying water to the state’s residents and ecosystems. The dramatic differences in climate from one place to another across Nevada are a direct result of its vast size and rugged topography, which spans elevations from roughly 500 feet near the Colorado River to over 13,000 feet in the White Mountains. Anyone who has traveled through high-country passes knows that elevation is a major driver of weather and climate, often bringing increased winds, colder temperatures, and a higher chance of precipitation.
Understanding the specific nevada climate and weather patterns means recognizing these regional variations. For example, while places like Boulder City experience hotter, drier conditions year-round due to lower elevation, mountain communities like Ely see significantly more precipitation and lower temperatures. This stark contrast across relatively short distances highlights the influence of elevation. If you’re exploring the state, checking the local forecast and understanding the specific climate of your destination, whether it’s the desert valleys or higher elevations, is crucial for a safe and enjoyable trip. Exploring specific regional climates like the [carson city nevada climate](https://lifetodiscover.com/carson-city-nevada-climate/) offers further insight into this state’s diversity.
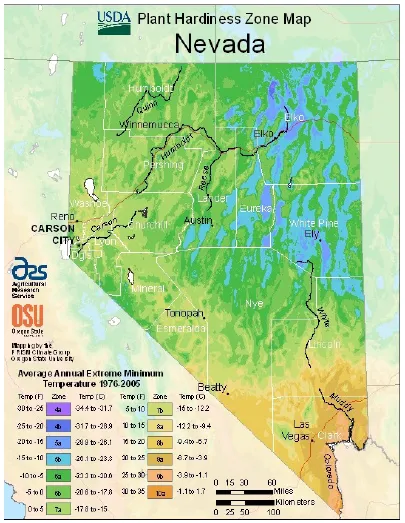
USDA Plant Hardiness Zone map for the United States, highlighting the varied climate zones across Nevada
Orographic lifting is another key climatic process in Nevada, especially along the Sierra Nevada Range. As moist air is pushed up against these steep mountains, it cools, and the moisture condenses, leading to precipitation on the windward slopes. This process leaves drier air to descend on the leeward side, creating a “rain shadow” effect in areas like the Great Basin, contributing significantly to Nevada’s overall aridity.
Key Climate Influences in Nevada
Large-scale atmospheric phenomena also impact nevada climate and weather. The El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO), with its warm (El Niño) and cool (La Niña) phases, significantly influences winter storm tracks. During El Niño, storms often shift southward, potentially bringing more precipitation to southern Nevada, while the impact on northern Nevada can vary. Conversely, La Niña years often mean drier conditions for southern Nevada. These climate cycles affect annual precipitation totals and the distribution of moisture across the state.
Atmospheric rivers, concentrated bands of water vapor associated with strong winds, are another critical factor, particularly for western Nevada and the Sierra. These events can bring intense precipitation, sometimes leading to floods and landslides, but they are also vital contributors to the overall water supply, especially for building the crucial mountain snowpack.
The Importance of Snowpack
Mountain snowpack acts as a natural reservoir, storing water through the winter and releasing it slowly as snowmelt in the spring and summer. This gradual release is essential for sustaining streamflow, supporting riparian habitats, and providing water for downstream communities, agriculture, and industry. The timing and amount of snowmelt directly influence water availability throughout the state, impacting everything from urban water use to recreational activities like rafting and fishing.
Navigating Hazardous Weather in Nevada
While Nevada is known for its dry climate, its weather can also be extreme and hazardous. Understanding these potential dangers is crucial for safety. The frequency and intensity of events like floods, droughts, fires, and heat waves are all aspects of the nevada climate and weather pattern.
Floods can occur suddenly due to intense rainfall, rapid snowmelt, or rain falling on snowpack. Areas previously affected by wildfires are particularly vulnerable to landslides during heavy rain events. Monitoring stream levels via hydrographs helps predict potential flooding, but being prepared for flash floods, especially in low-lying areas or canyons, is vital.
What to Eat in Fort Worth – A Culinary Deep Dive
Discover the Top Restaurants in Denver – A Culinary Journey
Discover Where to Visit in Las Vegas
Drought is a persistent concern in Nevada. While the state is naturally arid, periods of abnormally low precipitation coupled with high temperatures can severely impact water resources, agriculture, and recreation. The U.S. Drought Monitor tracks drought severity across the nation, providing weekly updates on conditions ranging from abnormally dry to exceptional drought. Understanding the current drought status is important for conservation efforts and planning outdoor activities. For instance, understanding the [temperature in pahrump nevada](https://lifetodiscover.com/temperature-in-pahrump-nevada/) and its context within broader drought conditions provides valuable local insight.
Wildland fires are a significant hazard, especially during dry, hot, and windy conditions. Low humidity, warm temperatures, and high winds create ideal conditions for fires to start and spread rapidly. While lightning can ignite fires, many are human-caused. Living With Fire programs offer crucial information on how to mitigate risks and stay safe in wildfire-prone areas. Discussing conditions that lead to fires often involves considering extreme temperatures, such as a [mesquite nv record high temperature](https://lifetodiscover.com/mesquite-nv-record-high-temperature/) which exacerbates dryness and increases fire risk.
Heat waves, extended periods of abnormally high temperatures, pose significant health risks. Extreme heat can stress ecosystems, livestock, and vulnerable populations, and can even be fatal. Staying hydrated, finding cool environments, and avoiding strenuous activity during peak heat are essential safety measures.
Tracking Nevada’s Environment
Collecting accurate weather and climate data is a collaborative effort. Volunteer networks, like the National Weather Service’s Cooperative Observer Program (COOP) and the Community, Collaborative, Rain, Hail and Snow (CoCoRaHS) network, provide invaluable daily reports on temperature and precipitation across the state. These observations, even reporting zero precipitation, are critical for understanding regional patterns.
Landscape condition monitoring, often using techniques like repeat photography, helps land managers track environmental changes over time, including the impacts of drought, fire, and recovery efforts. These local observations, combined with scientific data, provide a more complete picture of how nevada climate and weather variations affect the land and its resources. Reporting local conditions through platforms like CoCoRaHS or directly to the State Climate Office contributes to the body of data used for resource management and policy decisions. Documenting drought impacts from personal experience also provides valuable ground-level information for assessing severity and informing response efforts.
 Landscape photo taken in 2000 showing barren land after the Camp Creek Fire on Cottonwood Ranch, Nevada
Landscape photo taken in 2000 showing barren land after the Camp Creek Fire on Cottonwood Ranch, Nevada Landscape photo taken in 2015 showing successful recovery of native grasses on Cottonwood Ranch after a wildfire, demonstrating landscape monitoring
Landscape photo taken in 2015 showing successful recovery of native grasses on Cottonwood Ranch after a wildfire, demonstrating landscape monitoring
Conclusion
The nevada climate and weather present a compelling study in contrasts – extreme aridity alongside significant mountainous regions, scorching summers balanced by vital winter snows. Understanding these patterns, from the fundamental difference between weather and climate to the influence of topography, ENSO, and atmospheric rivers, is essential for appreciating the state’s dynamic environment. Being aware of potential hazards like floods, droughts, fires, and heat waves allows for safer travel and living.
The ongoing efforts of scientists and volunteer observers to monitor and document these conditions provide crucial insights for managing resources and adapting to future changes. Whether you’re planning a visit or calling Nevada home, a deeper understanding of its climate and weather will enrich your experience and appreciation for this extraordinary landscape.
