Michigan, often referred to as the Great Lakes State, boasts a climate profoundly shaped by its surrounding freshwater giants. Understanding the climate for Michigan is crucial for anyone planning a visit, considering a move, or simply interested in the state’s unique geography. It’s a climate of striking contrasts, featuring distinct seasons that offer a dynamic range of experiences throughout the year, from snowy winters perfect for ice fishing to warm, humid summers ideal for exploring the extensive coastlines. The Great Lakes act as natural moderators, influencing temperatures and precipitation patterns in ways that significantly differentiate coastal areas from inland regions. This creates a fascinating interplay between the environment and human life, impacting everything from agriculture to tourism and daily activities.
Key Characteristics of the Climate for Michigan
The climate for Michigan is characterized by its pronounced seasonality, a hallmark of its Midwest location. Winters are typically cold and snowy, while summers are warm and humid. However, the sheer size and thermal mass of the Great Lakes significantly moderate these extremes, particularly along the shorelines. Lake Michigan to the west and Lakes Huron and Erie to the east exert a tempering influence, making coastal areas milder in winter and cooler in summer compared to inland locations.
This moderating effect is clearly seen when comparing cities at similar latitudes. For example, Lansing, located centrally, experiences significantly more hot days and very cold nights annually than Muskegon on the Lake Michigan shore. The impact is even more dramatic in the Upper Peninsula along Lake Superior, where very hot days are exceptionally rare. Understanding these regional variations is key to appreciating the diverse climate for Michigan.
Historical Climate Trends in Michigan
Examining historical data reveals significant shifts in the climate for Michigan over the past century and beyond.
Temperature Changes
Temperatures across Michigan have shown a notable warming trend, increasing by nearly 3°F since the early 20th century. The 2000s stand out as the warmest decade on record, with 2012 being the hottest single year statewide. This warming has been most prominent during the winter and spring months, aligning with patterns observed across much of the Midwest. Summers, interestingly, have not warmed substantially, with the number of hot days generally below average since 1990. Conversely, the trend of warmer winters is reflected in a decrease in the number of very cold nights since 1990. This also correlates with a reduction in the average maximum ice cover on the Great Lakes compared to historical averages.
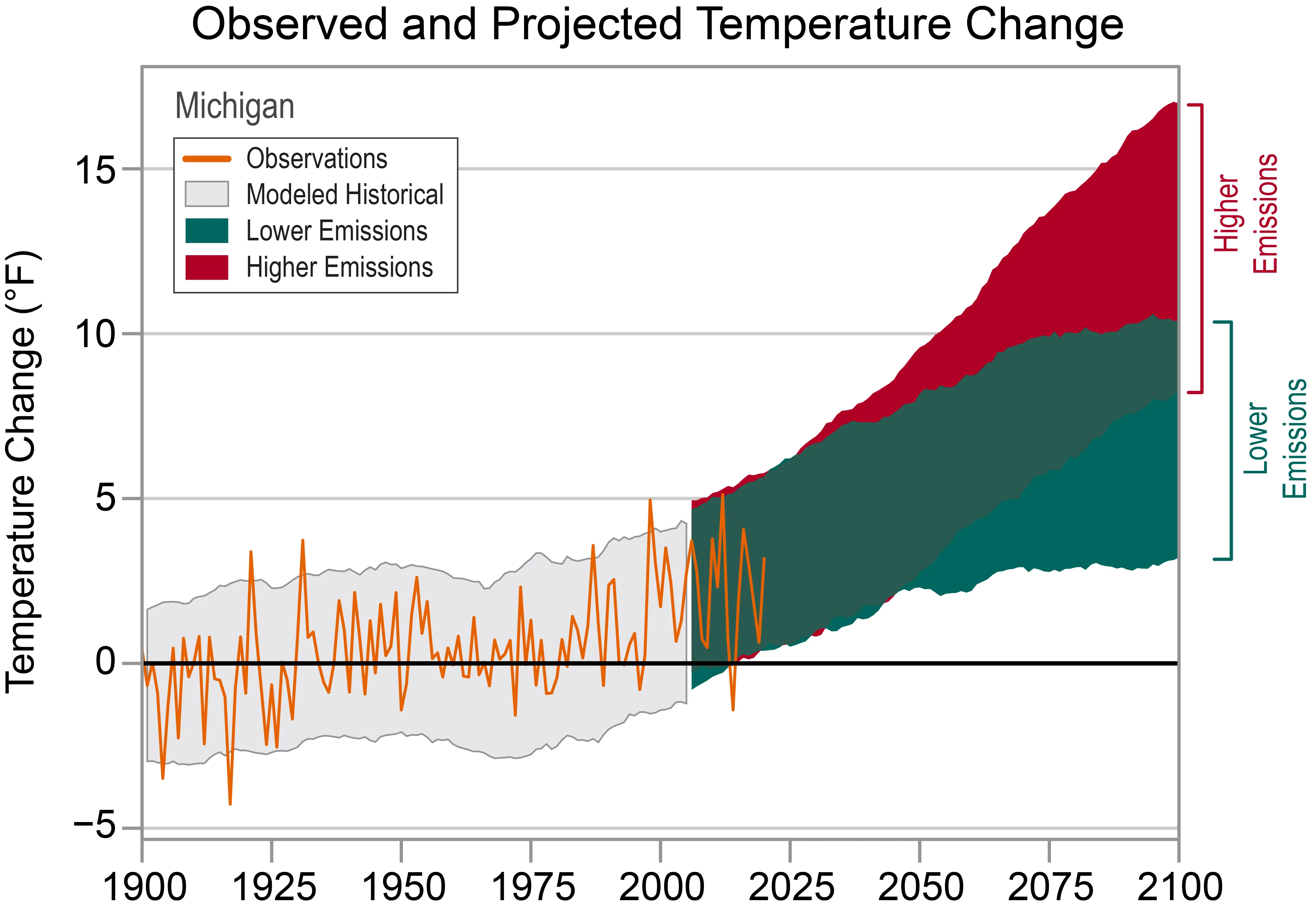 Observed and Projected Temperature Change in MichiganFigure 1: Historical and projected temperature changes for Michigan, showing a significant warming trend.
Observed and Projected Temperature Change in MichiganFigure 1: Historical and projected temperature changes for Michigan, showing a significant warming trend.
Precipitation Patterns
Annual precipitation in Michigan varies considerably year to year, with recorded extremes ranging from a low of 22.7 inches in 1930 to a high of 41.8 inches in 2019. While the 1930s and early 1960s saw the driest multiyear periods, the 2010s have been among the wettest, with the 2016–2020 period being the wettest consecutive 5-year interval on record. This variability is a key aspect of the climate for Michigan.
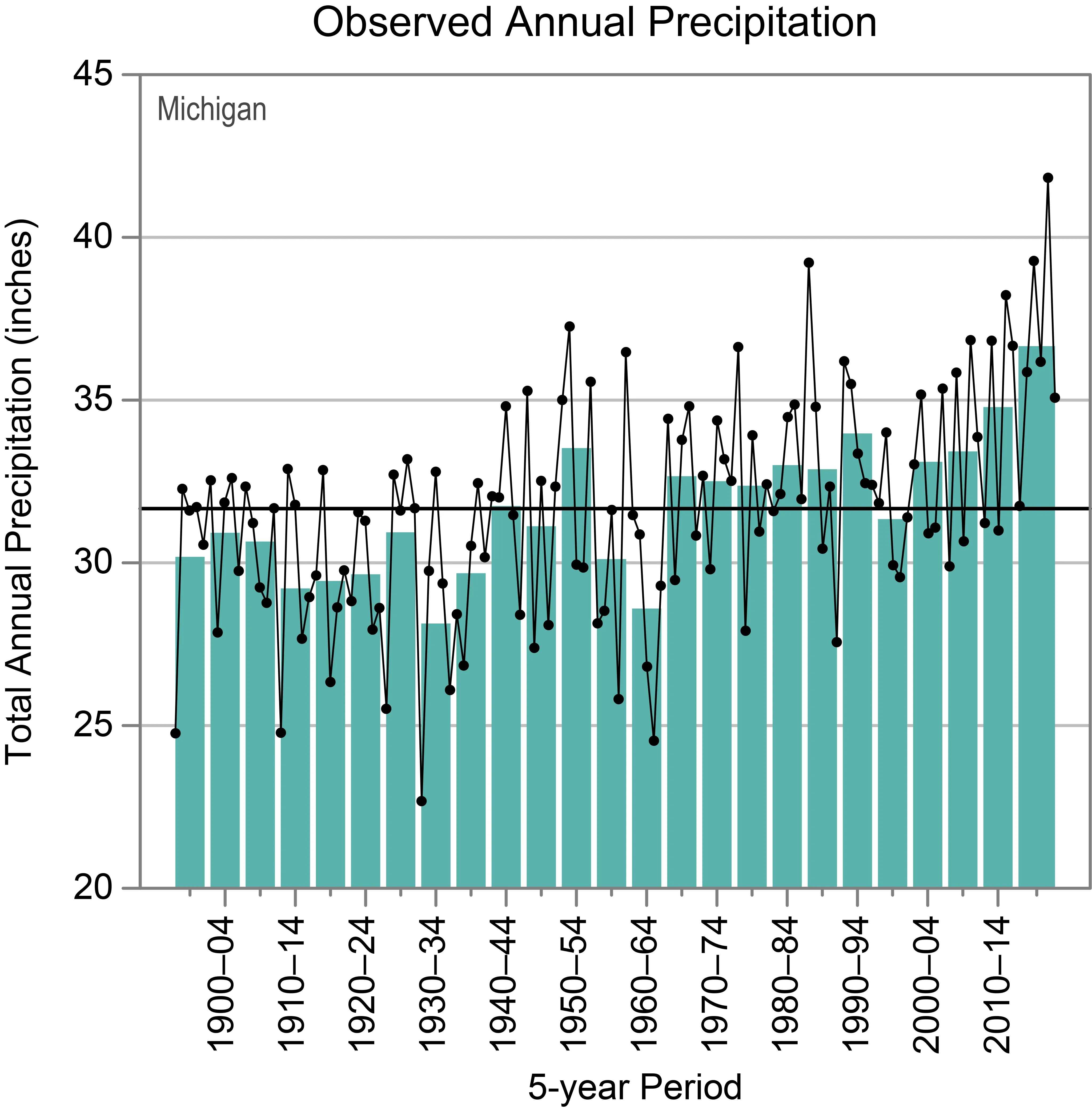 Observed Annual Precipitation in MichiganFigure 2d: Observed annual precipitation for Michigan from 1895 to 2020, indicating recent wetter periods.
Observed Annual Precipitation in MichiganFigure 2d: Observed annual precipitation for Michigan from 1895 to 2020, indicating recent wetter periods.
Extreme Weather Events
One significant trend in the climate for Michigan is the increasing frequency of extreme precipitation events. Days with 2 inches or more of precipitation have become more common, with the highest multiyear averages recorded in the 2010–2014 and 2015–2020 periods. These intense rainfall events can have considerable impacts on infrastructure and agriculture.
You can explore the climate in Detroit Michigan for a more focused look at urban weather patterns.
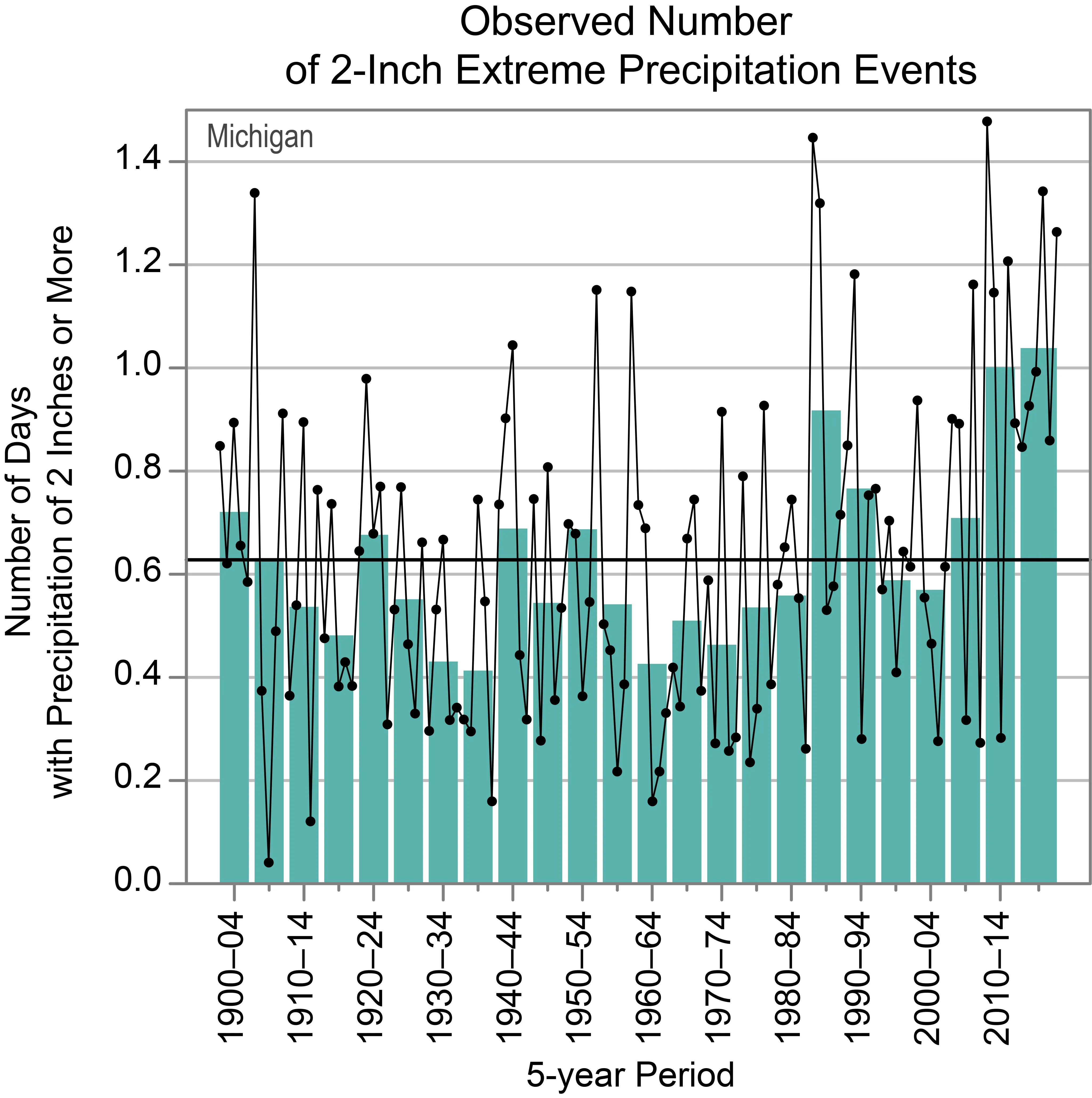 Observed Number of 2-Inch Extreme Precipitation Events in MichiganFigure 3: Observed annual number of 2-inch extreme precipitation events in Michigan, showing an increasing trend since 2000.
Observed Number of 2-Inch Extreme Precipitation Events in MichiganFigure 3: Observed annual number of 2-inch extreme precipitation events in Michigan, showing an increasing trend since 2000.
Great Lakes Water Levels and Ice Cover
Water levels in the Great Lakes, including Lake Michigan–Huron, have historically fluctuated significantly, ranging 3 to 6 feet since the late 19th century. After a period of notably low levels in the early 2000s, lake levels rose rapidly, reaching some of the highest recorded levels in 2020. Reduced winter ice cover, linked to warmer temperatures, also leaves shorelines more vulnerable to erosion and flooding from storms.
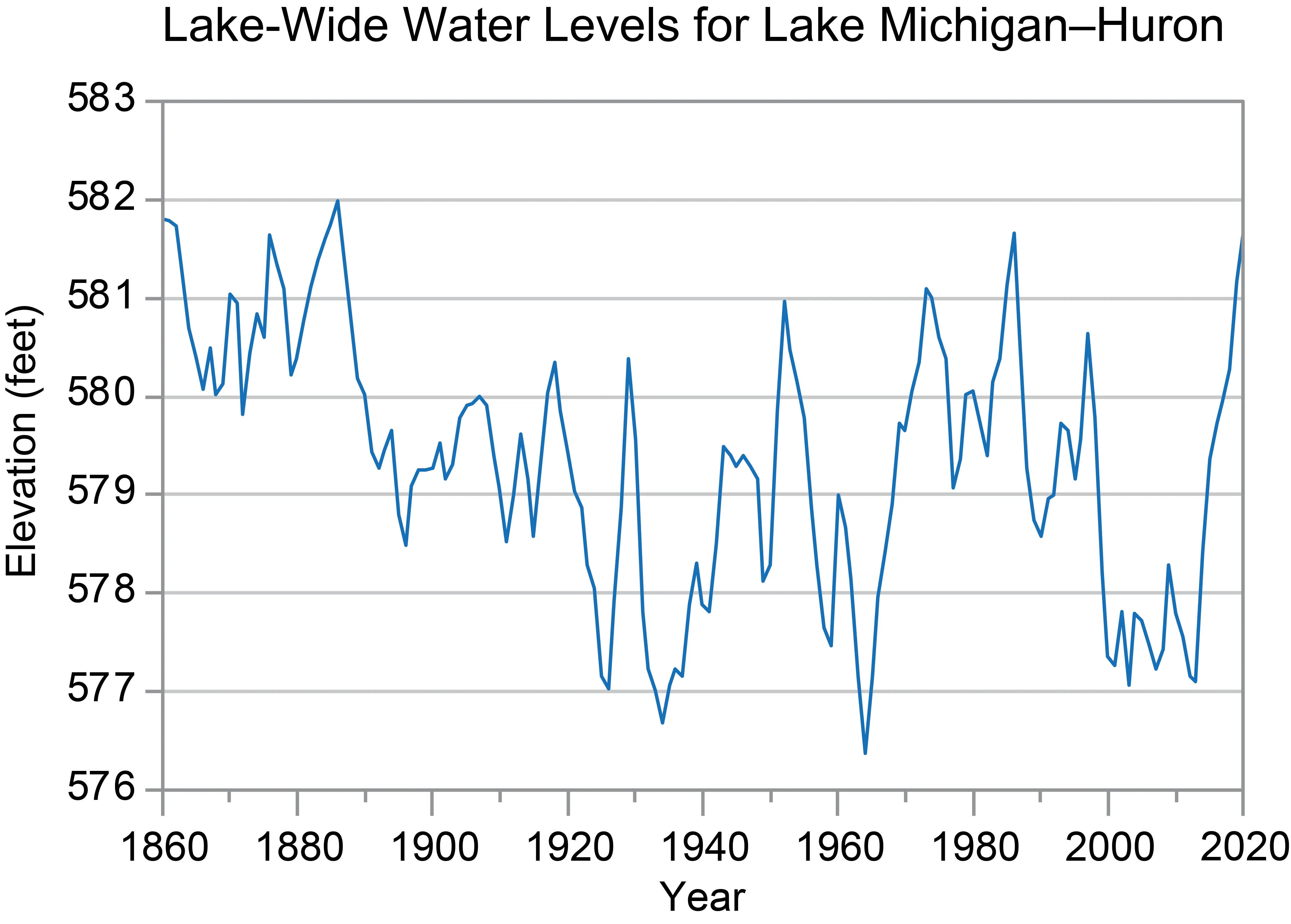 Lake-Wide Water Levels for Lake Michigan-HuronFigure 4: Annual water levels for Lake Michigan–Huron, showing historical fluctuations and the recent rise.
Lake-Wide Water Levels for Lake Michigan-HuronFigure 4: Annual water levels for Lake Michigan–Huron, showing historical fluctuations and the recent rise.
Projected Future Climate for Michigan
Climate models project continued changes in the climate for Michigan throughout this century, with potential impacts varying based on future greenhouse gas emission levels.
Future Temperature Projections
Under a scenario where emissions continue to increase, historically unprecedented warming is projected. Even with lower emissions, annual average temperatures are likely to exceed historical records. This warming poses particular risks for urban areas like Detroit, where the combination of high temperatures and humidity can lead to dangerous heat island effects. Rising spring temperatures, while potentially lengthening the growing season, also increase the risk of damaging late spring freezes, as dramatically demonstrated by the agricultural losses in 2012.
Future Precipitation and Extreme Events
Projections indicate an increase in overall precipitation for Michigan, primarily expected during the winter and spring months. The frequency and intensity of extreme precipitation events are also projected to rise. This could lead to more frequent and intense flooding, presenting challenges for urban drainage and posing threats to the state’s vital agricultural sector by potentially delaying planting and impacting crop yields. For a specific location, understanding the climate in Ann Arbor Michigan can provide localized insights.
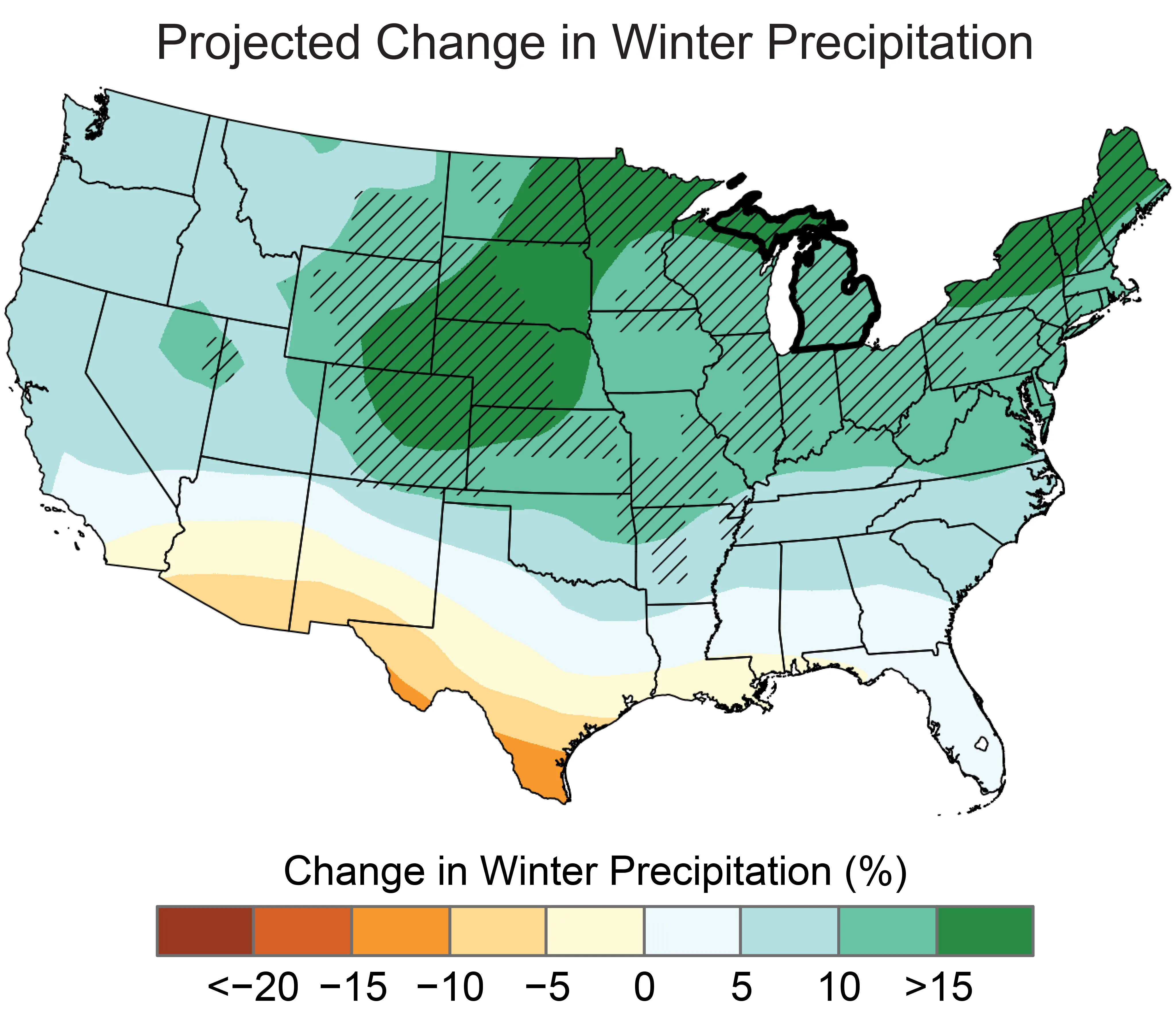 Projected Change in Winter Precipitation for MichiganFigure 5: Projected changes in total winter precipitation for Michigan by the middle of the 21st century under a higher emissions pathway.
Projected Change in Winter Precipitation for MichiganFigure 5: Projected changes in total winter precipitation for Michigan by the middle of the 21st century under a higher emissions pathway.
Future Drought Intensity
Despite projected increases in precipitation, the intensity of future summer droughts is likely to increase. Rising temperatures will lead to higher evaporation rates from both land and water surfaces. This increased water loss means that even with more rainfall overall, periods of dry weather during the summer could result in more severe soil moisture deficits, intensifying drought conditions, which are already a natural part of the climate for Michigan.
Impacts on Great Lakes
Changes in temperature, precipitation, and evaporation rates will continue to influence water levels in the Great Lakes. Both historically high and low lake levels have caused significant environmental and socioeconomic problems, from shoreline erosion and flooding during high water periods to issues with water supply, shipping, and wetlands during low water periods. Future fluctuations remain a subject of ongoing research, but the vulnerability of coastal areas to changes in lake levels and reduced ice cover highlights the interconnectedness of the climate for Michigan and its most iconic natural feature. You can also look into the Lansing Michigan climate for another inland perspective.
Planning Your Visit Based on the Climate for Michigan
Understanding the climate for Michigan is essential when planning your travels. Each season offers unique beauty and activities. Summer is perfect for enjoying the lakes and outdoor festivals, while fall brings stunning foliage. Winter is ideal for snow sports, and spring offers blossoming landscapes. Being aware of the typical weather patterns and potential for extreme events during your chosen travel time ensures a more prepared and enjoyable experience. Whether you’re exploring where to go in Detroit Michigan or heading north, checking the local forecast is always recommended.
Conclusion
The climate for Michigan is a complex and dynamic system, heavily influenced by the vast Great Lakes. From historical warming trends and changing precipitation patterns to future projections of increased extremes, understanding these climatic shifts is vital. This knowledge not only provides insight into the environmental changes shaping the state but also helps inform decisions related to agriculture, urban planning, and, of course, planning your next unforgettable Michigan travel adventure. The story of Michigan’s climate is an ongoing narrative of interaction between land, water, and atmosphere, offering endless fascination for residents and visitors alike.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main seasons like in Michigan?
Michigan experiences four distinct seasons. Winter is cold and snowy, especially in areas receiving lake effect snow. Spring is cool and transitions to milder temperatures. Summer is warm and humid, ideal for water activities. Fall is crisp and cool, famous for vibrant fall foliage.
How do the Great Lakes affect the climate for Michigan?
The Great Lakes moderate temperatures. They keep shorelines warmer in winter and cooler in summer compared to inland areas. They also contribute to lake effect snow downwind of the lakes, particularly in the western Upper Peninsula and along the Lake Michigan shore.
Is Michigan’s climate changing?
Yes, observations show that temperatures in Michigan have risen significantly since the early 20th century, especially in winter and spring. There has also been an increase in the frequency of extreme precipitation events.
What are the projected future climate trends for Michigan?
Future projections indicate continued warming, with potential for historically unprecedented temperatures under higher emissions scenarios. Precipitation is projected to increase, particularly in winter and spring, alongside more frequent and intense extreme precipitation events.
How does climate affect agriculture in Michigan?
Climate impacts Michigan’s agriculture significantly. Warmer springs can bring early blooms but also increased risk of damaging late freezes. Changes in precipitation patterns and increased drought intensity can affect crop yields. Extreme rainfall can lead to flooding, delaying planting or causing crop loss.
What are the impacts of climate change on the Great Lakes?
Changes in temperature, precipitation, and evaporation affect Great Lakes water levels, impacting shipping, infrastructure, and ecosystems. Reduced winter ice cover due to warming leaves shorelines more vulnerable to erosion and flooding.
